Constructs the set-theoretic intersection between an array of geometries and another geometry.
Intersect(SpatialReference SpatialReference, Geometry[] InGeometryArray1, Geometry InGeometry2)
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
SpatialReference |
The spatial reference of the geometries in the InGeometryArray1. This cannot be null. |
|
InGeometryArray1 |
An array of points, multipoints, polylines or polygons. The input types can be mixed. |
|
InGeometry2 |
A single geometry of any type. |
Return Value
An array of geometries (Geometry[]).
Remarks
This operation constructs the set-theoretic intersection between each element of the input array and InGeometry2.
Each result is placed at the corresponding index in the output array &endash; that is, Result[i] = InGeometryArray1[i] Intersect InGeometry2.
Any inputs that are completely outside InGeometry2 are represented by empty geometries of the same type in the output array.
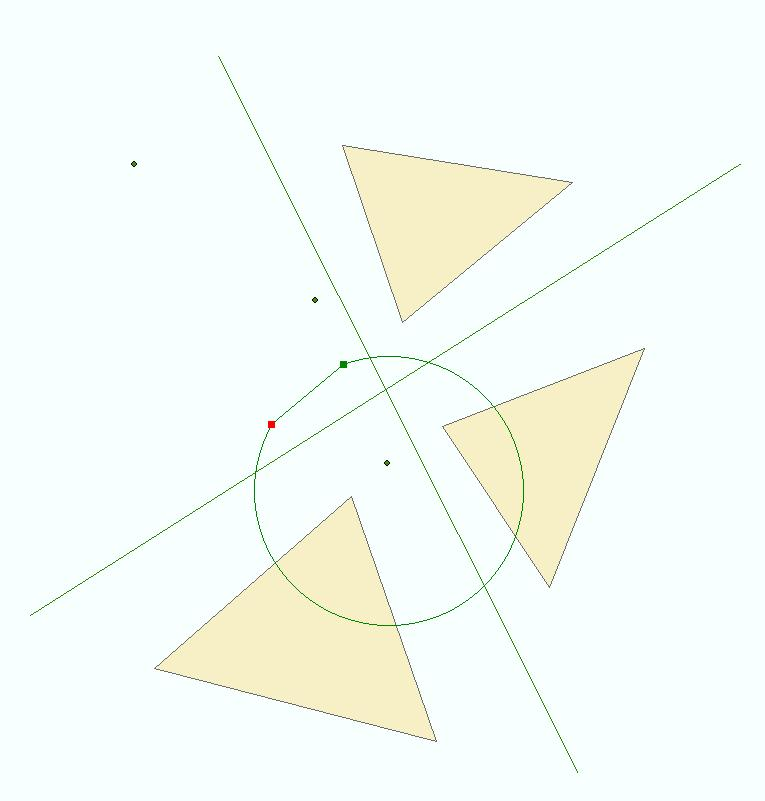
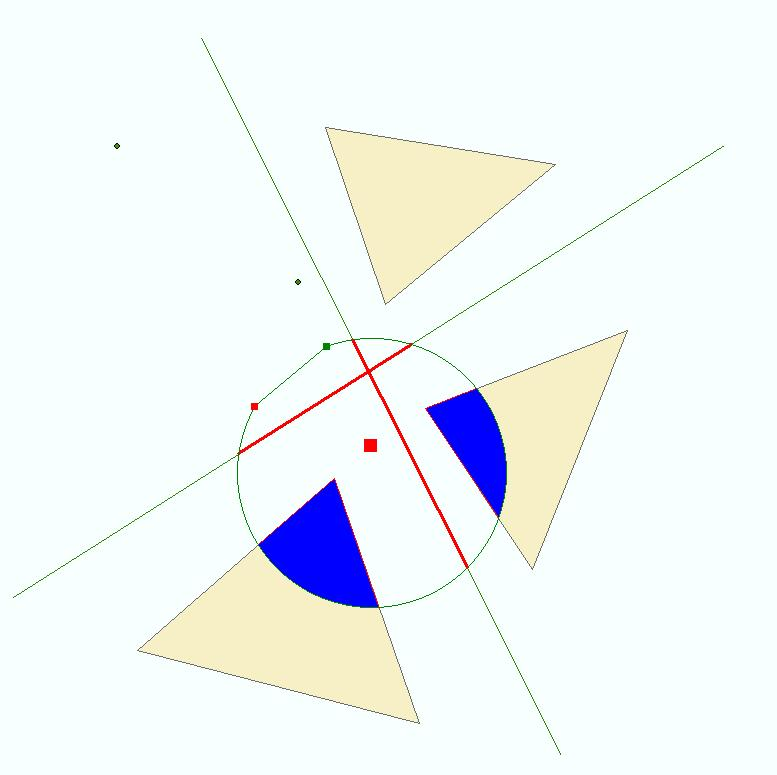
The figure below shows an example of the intersect operation. The input geometry array contains all geometries shown on the left of the figure with the exception of the central circular polygon. The output array contains the modified geometries shown in the right part of the figure. Note that two of the output points will be "empty" because their corresponding inputs are outside the circular polygon.
|
|
|
Figure 1 - The intersect operation applied to a collection of points, lines and polygons.