Geometry Service Simplify method
Generates topologically correct geometry.
Simplify(SpatialReference
SpatialReference, Geometry[]
InGeometryArray)
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
SpatialReference |
The spatial reference
of the geometries in the InGeometryArray.
This cannot be null. |
|
InGeometryArray |
The array of Geometry
to be simplified. All geometries are assumed to
be in the coordinate system defined by the SpatialReference
parameter. |
Return Value
An array of geometry (Geometry[]).
Remarks
Input geometry can be points, multipoints,
polylines or polygons. Geometry that cannot be simplified are replaced
with empty geometries of the same type. This operation uses the coordinate
grid and the XY and Z cluster tolerances of the spatial reference. For
more information on these properties and how they can affect your coordinates,
please refer to the ESRI whitepaper, Understanding
Coordinate Management in the Geodatabase.
Simplify alters the input geometry making its
definition "topologically legal" with respect to its geometry
type:
For Points, Simplify does nothing.
A point has no constraints on the values of its coordinates.
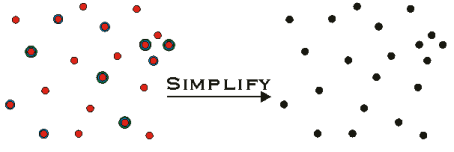
For Multipoints, Simplify snaps
all X, Y, Z, and M coordinates to the grid of the associated spatial reference
(defined by the spatial reference’s false origin and XY Units),
then removes identical points. A point is identical to another point when
the two have identical X and Y coordinates (after snapping), and when
attributes for which it is aware are identical to the attributes for which
the other point is aware. For example, if both points are Z aware, the
Z coordinate values must be identical.
For Polylines, very little
is done. Coordinates are snapped, zero-length segments and empty parts
are removed. Length is determined in 3D if the polyline has z coordinates,
otherwise it is determined in 2D.
For Polygons, Simplify identifies
an interior and exterior for the polygon, then modifies the polygon structure
to be consistent with that determination. The methodology for identifying
interior and exterior is:
1. Remove all dangles.
2. Identify the largest
legal rings, add them to the output version of the polygon, then delete
them from the working version.
3. Repeat.
This operation uses the
XY cluster tolerance of the associated spatial reference to determine
when two vertices are the same, or when a vertex
needs to be snapped to a line. This specific approach is subject to change
in future releases of ESRI software.
At the end of Simplify,
no rings will overlap, no self intersection will occur (except in certain
circumstances) and, in general, an arbitrary point can always be classified
unambiguously as either outside, on the boundary of, or inside the polygon.
All exterior rings are oriented clockwise. All
interior rings (i.e. holes) are counter-clockwise.
|
|
|
|
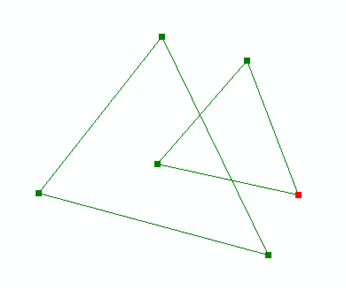
Linework input to the polygon simplify operation |
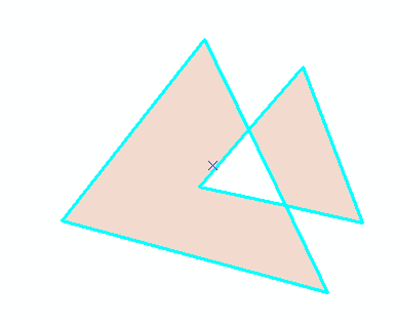
Polygon created via the simplify operation. |
Examples


