Base Type:
Polycurve
Derived Types: PolygonB, PolygonN
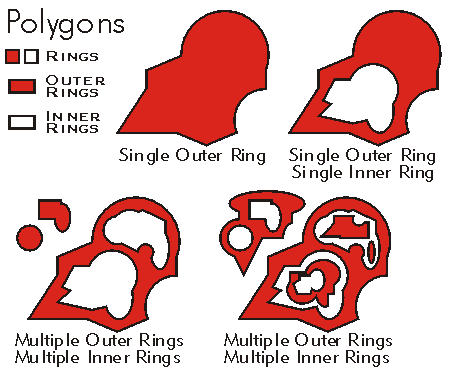
An abstract class that serves as a base to its derived types, representing a collection of one or more exterior and interior rings. .
Remarks
The rings do not need to be connected to or
contained by other rings in the polygon. However,
all rings are considered to be part of a single polygon regardless of
their location. Rings can be embedded in the interior
of other rings. Embedded rings define interior
boundaries or holes within the polygon. Exterior
rings are oriented in a clockwise direction while interior rings are oriented
counterclockwise.
In general, you will work with the normalized polygon type PolygonN,
whether creating a polygon or working with a polygon returned from a service
request. See the discussion
on binary and normalized geometry for more information. When
constructing a PolygonN with overlapping
rings in the same direction, the server will simplify the polygon for
you. If two rings overlap, the overlapping area
will be considered an interior ring (hole). If
three rings overlap, the overlapping area will be considered an exterior
ring and so on.
